Technology
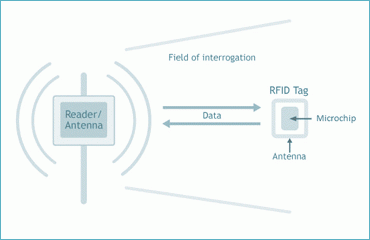
Radio Frequency Identification (RFID) is a contactless communication technology, that requires no line of sight to identify objects.
The exchange of information through wireless technology (electromagnetic waves) is extremely versatile. Information is stored on a chip, which is embedded in a label. Data can be read or rewritten to the chip. Passive tags can be read from a distance of 3 cm up to 8 meters.
Communication
A RFID read/write device creates a weak electro-magnetic field and sends a message to the environment, asking if there is a RFID tag out there. The tag responds to the signal and sends information to the back end, or receives data i.e. information being written to the chip. A line of sight is not required for communication between the RFID read/write device and the RFID label.
Applications
RFID is a versatile technology that is used in an array of industrie verticals and applications.
Listed below are a few application examples, however these are by no means exhausted:
- Intralogistics
- Libraries
- Supply chain management
- Document tracking and tracing
- Production
- Warehousing
- Brand protection
- Palette identification
- Theft prevention
- Inventory Management